How to Stop Leg Cramps Immediately: Effective Home Remedies and Prevention Tips
Introduction
Leg cramps are a common yet highly disruptive issue that affects millions of people unexpectedly. The sharp, intense pain can be overwhelming, whether it strikes in the middle of the night or during physical activities. If you've ever been woken up by sudden cramping, you know how important it is to find relief fast.
But how do you stop leg cramps immediately, and can they be avoided altogether?
Let's take a deeper understanding of what causes them, the symptoms, and practical ways to get rid of leg cramps for good.
Understanding Leg Cramps: What Are They?
Leg cramps, also known as muscle spasms, are sudden and involuntary contractions of one or more muscles, commonly occurring in the legs. They usually affect the calves, but can also occur in the thighs or feet. The intense tightening sensation can leave you unable to move, and although the spasm usually goes away within minutes, the lingering soreness can last for hours.
If you want to know how to stop leg cramps immediately, it's important to first understand what causes them.
What Causes Leg Cramps?
1. Poor Blood Circulation

One of the main reasons for leg cramps is poor circulation. Blood circulation is less effective in the lower extremities because they are farthest from the heart.
Diabetes and high cholesterol can both lead to poor blood circulation. It's important to be aware that diabetes medication can cause neuropathy, which is a tingling sensation in the hands and feet, as it weakens the nerves. [1] This is why diabetic patients may undergo foot amputations or experience slow healing of injuries, as the nerves are unable to supply blood to those areas of the body. To relieve nerve pain, consider using R-Lipoic Acid supplements, which can help with leg cramps and neuropathy. [2]
If you are taking cholesterol or blood pressure medication, consider stopping it. Why?
Because these medications can lead to irritation, headaches, and affect the brain. Instead, opt for healthy fats such as desi ghee, beans, and legumes, which can help increase good cholesterol in your body. You may also find it helpful to watch my video on the dangerous side effects of cholesterol medication.
2. Blocked Arteries
A blocked artery in your body can lead to leg cramps. Peripheral Artery Disease is a condition that affects the blood vessels supplying blood to the legs and feet. It is caused by the narrowing of nerves and blood vessels in the legs, leading to reduced blood flow that can damage nerves and other tissues. [3]
This occurs when fatty material, known as plaque, builds up on the artery walls, causing them to narrow. The artery walls also lose their flexibility to expand and allow increased blood flow when necessary.
3. Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolytes, such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium, are essential for proper muscle function. When these minerals are out of balance, it can lead to muscle cramping because the muscles are unable to contract and relax effectively. [4] Dehydration or certain medications can lower electrolyte levels, increasing the likelihood of cramps.
4. Pregnancy
During pregnancy, leg cramps are common, particularly in the third trimester. The increased weight and pressure on the nerves, along with potential deficiencies in key nutrients like magnesium, can lead to cramping, especially at night. [5]
5. Overuse of Muscles
Vigorous exercise, especially without proper warm-up or cool-down, can strain the muscles, leading to cramps. This is particularly common among athletes or those who engage in high-intensity activities.
6. Too Much Calcium
Overconsumption of calcium, often known as hypercalcemia, can disrupt magnesium levels, leading to muscle cramps.[6] Calcium aids in muscle contraction, but excessive intake without sufficient magnesium can cause prolonged muscle contractions or spasms.
7. Medications and Health Conditions
Certain medications, such as those for blood pressure and cholesterol, can cause leg cramps as a side effect. Additionally, conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD) can lead to reduced blood flow in the legs, increasing the risk of cramps.
How to Stop Leg Cramps Immediately?: Home Remedies
The good news is that most leg cramps typically stop immediately on their own within about 10 minutes. However, the discomfort and tightness from a leg cramp can linger for up to 24 hours.
Luckily, there are several home remedies for leg cramps that can assist in treatment. Here are some effective strategies to get rid of leg cramps:
1. Hydration

Dehydration is a common trigger for muscle cramps, so it"s crucial to stay hydrated throughout the day. Drinking water before, during, and after exercise can help maintain proper muscle function. Electrolyte-rich beverages, such as coconut water, can be particularly beneficial if you sweat a lot, as they replenish lost minerals like potassium and magnesium.[7]
2. Stretching and Light Exercise
Stretching is one of the quickest ways to stop a leg cramp in its tracks. As soon as you feel a cramp coming on, gently stretch the affected muscle. For example, if the cramp is in your calf, pull your toes upward toward your shin. Stretching before and after exercise can also help remove cramps from the legs.
Regular exercise, such as yoga and walking, improves blood circulation and reduces cramp likelihood. Focus on leg exercises for muscle flexibility and strength.
3. Warm Compress or Massage

Applying a warm compress or heating pad to the affected muscle can help relax tight muscles.
Alternatively, a gentle massage can stimulate blood flow and reduce muscle tension. If you experience frequent cramps, consider regular massages to keep the muscles loose and prevent recurrence.
4. Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV)
Apple cider vinegar is a natural remedy that can help balance your body"s pH levels. High alkalinity can sometimes cause muscle cramps, and consuming ACV helps lower pH levels. A tablespoon of ACV diluted in a glass of warm water before bedtime can help prevent nighttime leg cramps.[8]
5. Increase Magnesium Intake
Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals for muscle function. It aids in muscle relaxation, so ensuring you get enough magnesium can help prevent cramps. Foods rich in magnesium include dark leafy greens, almonds, avocados, and bananas. If you"re not getting enough from food alone, magnesium supplements can help.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like salmon, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, help reduce inflammation and improve blood flow, making them excellent for cramp prevention. If natural food sources are insufficient, consider an Omega-3 supplement to support muscle health.[9]
Consuming Omega-3-rich foods, such as salmon, chia seeds, and flax seeds, will help thin your blood and minimize nerve pain. Since it's difficult to acquire enough Omega-3s from natural foods, consider taking an Omega-3 supplement.
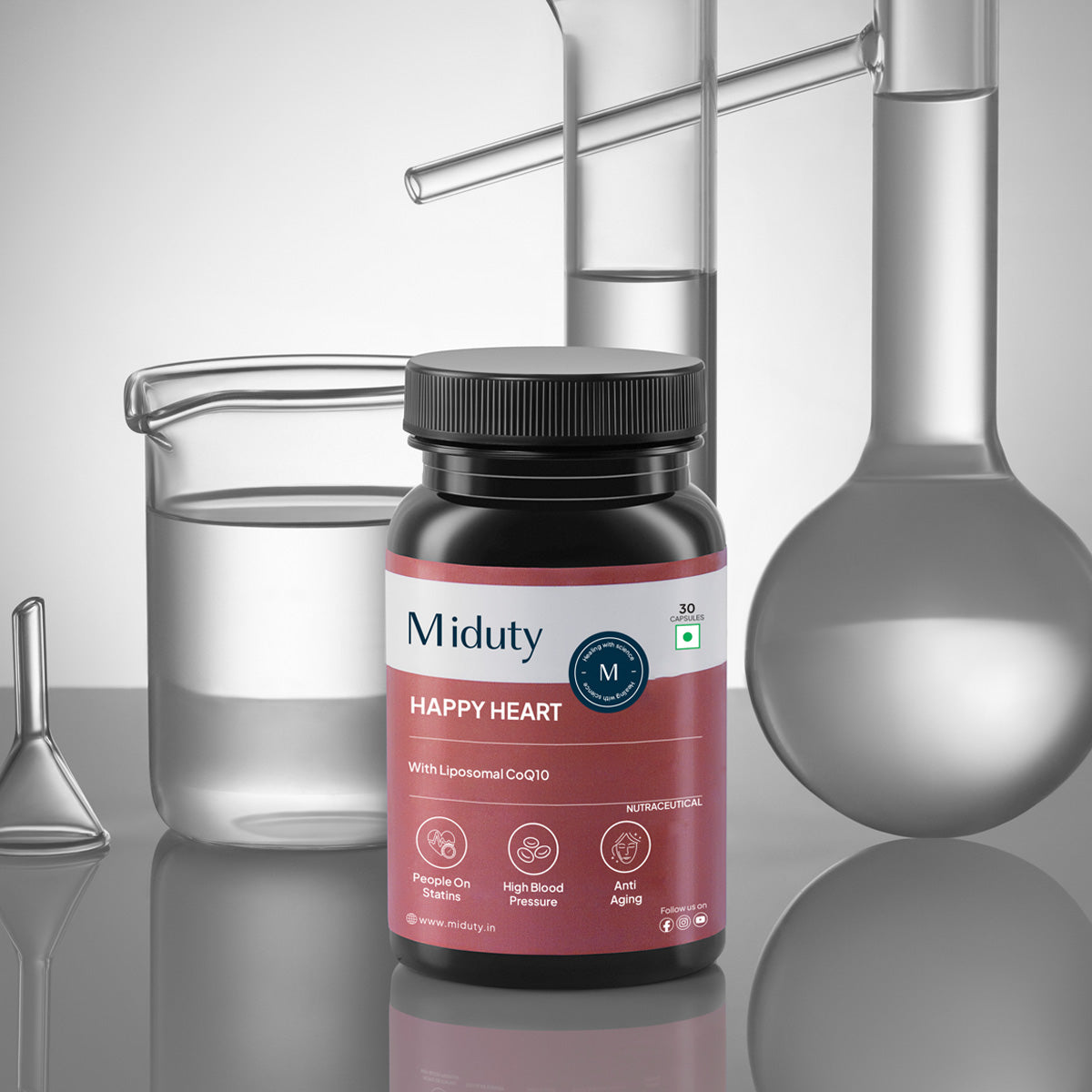
7. CoQ10 for Older Adults
CoQ10 is an antioxidant that supports energy production in muscles. For older adults, it can be especially helpful in preventing cramps caused by poor circulation or muscle fatigue.
CoQ10 supplements, particularly in liposomal form, are highly absorbable and can boost cardiovascular health as well as prevent muscle cramps.
How to Get Rid of Leg Cramps at Night?
Nighttime leg cramps, also known as nocturnal cramps, can be particularly disruptive.[10]
Here are some tips specifically for those late-night cramps:
1. Stay Active During the Day
Prolonged periods of inactivity can increase the risk of cramps at night. Regular movement during the day, such as walking or light stretching, can help keep your muscles flexible and prevent cramps while you sleep.
2. Elevate Your Legs Before Bed

If poor circulation is a concern, try elevating your legs for 10-15 minutes before bed. This encourages blood flow to the lower extremities.
3. Wear Compression Socks
Compression socks help improve circulation and are particularly useful if you experience frequent leg cramps or if you stand for long periods during the day.
When to Worry About Leg Cramps?
Most leg cramps are harmless, albeit painful.
If you are not able to stop leg cramps immediately with home remedies and get better with drinking water, exercising, or stretching, it could be a sign of an underlying health issue like diabetes, kidney disease, or nerve damage.
If your cramps come with swelling, redness, or warmth in the leg, it's important to seek medical advice right away, as these could be signs of a more serious problem like a blood clot or deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Conclusion
Understanding how to stop leg cramps immediately and manage their underlying causes can greatly improve your quality of life. Whether it's through maintaining proper hydration, stretching regularly, or increasing your intake of essential minerals like magnesium, these remedies can help you find relief and prevent future cramps.
If you find that cramps persist despite following these steps, consult a healthcare professional to rule out more serious conditions.
By incorporating these simple changes into your daily routine, you can stay active and pain-free, ensuring that leg cramps no longer interrupt your life.
References
|
Sr. No. |
Reference Links |
| 1. |
|
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. | |
| 7. | |
| 8. | |
| 9. | |
| 10. |

Diwali Detox & Radiance Bundle
Reclaim your glow this festive season with Miduty’s special Diwali bundle, a 3-in-1 formula that brings together three powerful supplements: Miduty Liver Detox, Miduty Stop Ageing, and Miduty Liposomal Glutathione to support your body through the festive hustle.
This Diwali, give yourself the gift of more energy, clearer skin, better detox, and deeper cellular health.